

 Vol. 39 (Number 12) Year 2018. Páge 12
Vol. 39 (Number 12) Year 2018. Páge 12
Yury I. TRESHCHEVSKY 1; Nadezhda A. SEREBRYAKOVA 2; Galina V. GOLIKOVA 3; Svetlana A. VOLKOVA 4; Tatiana A. VOLKOVA 5
Received: 01/11/2017 • Approved: 30/11/2017
ABSTRACT: Small and medium business constitutes not only the economic basis of a state but creates additional jobs, providing employment of the population, which leads to the necessity for development of a system of measures for state support of entrepreneurship, which is very important for further development of the state and creates scientific interest to this problem. The purpose of this research is to study the forms and method of support for small and medium entrepreneurship in the RF and to evaluate their effectiveness. The authors use the economic & statistical means of the research, as well as economic and comparative analysis. The research and practical developments are based on the following approaches: complex and structural & logical, the methods of comparison and modeling. The authors determine the top-priority directions for further development of small and medium entrepreneurship by means of such tools as development of public-private partnership, which raises the trust of business to the state; expansion of venture business, provision of the system of subsidies to small innovational companies, increase of information access of the system of state support and guarantees. The given recommendations could be used during solving the issues related to increase of the effectiveness of the methods for state support for small and medium business. |
RESUMEN: Las pequeñas y medianas empresas constituyen no solo la base económica de un Estado sino que crean puestos de trabajo adicionales, proporcionando empleo a la población, lo que lleva a la necesidad de desarrollar un sistema de medidas para el apoyo estatal al emprendimiento, que es muy importante para un mayor desarrollo del el estado y crea interés científico para este problema. El propósito de esta investigación es estudiar las formas y el método de apoyo para la pequeña y mediana empresa en la RF y evaluar su efectividad. Los autores utilizan los medios económicos y estadísticos de la investigación, así como el análisis económico y comparativo. La investigación y los desarrollos prácticos se basan en los siguientes enfoques: complejos y estructurales y lógicos, los métodos de comparación y modelado. Los autores determinan las direcciones de mayor prioridad para un mayor desarrollo de la pequeña y mediana empresa mediante herramientas tales como el desarrollo de asociaciones público-privadas, lo que eleva la confianza de las empresas hacia el estado; expansión de negocios de riesgo, provisión del sistema de subsidios a pequeñas empresas innovadoras, aumento del acceso a la información del sistema de apoyo y garantías estatales. Las recomendaciones dadas podrían usarse durante la resolución de los problemas relacionados con el aumento de la efectividad de los métodos de apoyo estatal para las pequeñas y medianas empresas. |
At the modern stage of development, the main goal of the state is the growth of the living standards of the population. For that, a system of methods and tools is developed, which should ensure increase of the population’s living standards. Thus, at present, there’s a complex of economic and administrative levers: the Strategy of socio-economic development of the Russian Federation, socio-oriented federal targeted programs, and the system of support for population at the regional and local levels. We think that an important reserve for provision of the growth of the living standards is state support for entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship in the macro-economic aspect is the factor that ensures the growth of economy and the growth of the living standards of the population; in view of the micro-economic studies, it is a factor that stimulates the expression of the citizens’ personal initiative for increase of the personal living standards. Obviously, not everyone is inclined to be involved in entrepreneurial activity, and, according to the psychologists’ data, 30% of people do not have skills for entrepreneurship (Tamoshina et al., 2012). Still, by supporting the entrepreneurial initiative, the state can reduce the load on social funds and stimulate the improvement of the psychological climate in the society.
In the conditions of crisis phenomena in the Russian economy, support for entrepreneurial activity is given a lot of attention. This study aims at monitoring of the effectiveness of state programs of support for small and medium business.
Studying the normative and legal documents allowed for the conclusion that the system of state support for entrepreneurial activity unites the complex of tools used both at the federal and the regional levels. According to the Law No. 209 –FZ “On development of small and medium entrepreneurship in the Russian Federation”, state support is based on the following principles:
- the declarative order of application of the subjects of small and medium entrepreneurship (SME);
- accessibility of the infrastructure of support for subjects of SME;
- equal access of subjects of SME to participation in the state programs;
- provision of support with observation of the requirements of the Federal law dated July 26, 2006, No. 135- FZ “On protection of competition”;
- openness of the procedures of provision of support (Federal law “On development of small and medium entrepreneurship in the Russian Federation” No. 209-FZ).
In the Russian Federation, there following forms of support for development of SME are determined:
- financial support (subsidies, budget investments, state and municipal guarantees for obligations of the subjects of SME which create the infrastructure of SME; assets of the federal budget provided to the state funds of scientific, scientific & technical, and innovational activity);
- property support (assignment for use of state and municipal property on a paid, free, or subsidized basis);
- information support (creation of the information systems, official web-sites for support for SME, etc. at the federal, regional, and municipal levels);
- consultation support (compensation of costs for payment for consultation services, creation of organizations that provide consultation services).
At the state level, support for entrepreneurial activity is performed on the basis of the laws, which include the state program “Economic development and innovational economy”, passed by the Decree of the Government of the RF dated April 15, 2014 No. 316, which contains the sub-program “Development of small and medium entrepreneurship” (Federal portal of small and medium entrepreneurship).
In view of the analytical information of the sub-program realization, it should be noted that over the 10-year period the volumes of investments grew, except for 2016, when financing was reduced by more than 30 % (Figure 1).
Figure 1
Assets of the federal budget used for implementation of the sub-program
“Development small and medium business in the RF” in 2005-2016 [3]
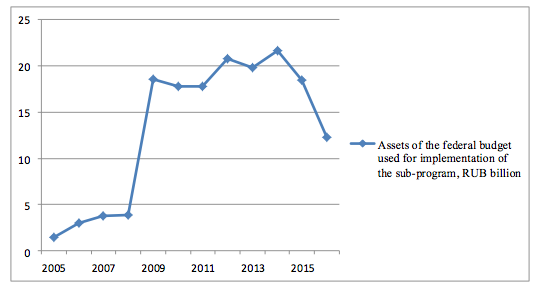
The implementation of the state program in 2016 involved 85 subjects of the Russian Federation, while in 2005 this number equaled 55 (The official web-site of the Federal State Statistics Service). Analyzing the indicators of demography of the organizations on the whole for the Russian Federation, it should be noted that in the period of 2005-2015 the peak of creation of organizations was in 2006, and 2009 marked a large reduction of the coefficient – which could be explained by the crisis phenomena in economy. The situation stabilized and the growth of the number of registered companies was marked again in 2015 (Figure 2).
Figure 2
Indicators of the demography of organizations of the Russian Federation in 2005 -2015 [3]

The dynamics of the coefficient of official liquidation of organizations is unstable, and 2006-2007 marked the growth of the number of liquidated organizations, with the second wave coming in 2011-2014; this process slowed down only in 2015. The indicators of the organizations demography reflect the reaction of the entrepreneurial sector to the economic situation in the country and are a barometer of the level of favorableness of conditions for doing business. According to the Government of the RF for 2015, the implementation of this program allowed achieving the expected results for 43 out of 69 indicators (The official web-site of the Federal State Statistics Service). At the same time, the planned indicators were not achieved for the following parameters:
- “Share of the average number of employees (without external part-time employees), employed at micro-, small and medium enterprises and with individual entrepreneurs, in the total number of the employed population” – deviation from the plan – 2 %;
- “Number of subjects of small and medium entrepreneurship (including individual entrepreneurs) per 1,000 people of the population of the Russian Federation” – deviation of 7.6 %.
Non-achievement of the targeted values of the indicators that characterize entrepreneurship shows the insufficient effectiveness of the program in this sector. However, the existing situation is predetermined by the general macro-economic situation, the external sanctions, and other circumstances (Serebryakova et al., 2016).
According to the report prepared for the Ministry of Economic Development, the effect from implementation of the Program of support for small and medium business is evaluated as positive. In particular, growth of GDP by 1 invested ruble constitutes RUB 27.6, and the revenues from the turnover of SME grew by 3% in 2015, as compared to 2013. The study of effectiveness of realization of the support forms allows for the conclusion that consultation support is the most effective, with expert support being the second. At that, financial support is peculiar for the negative dynamics. According to this source, with the annual budget of the Program of RUB 22 billion, the effect for GDP constitutes RUB 607 billion, and the effect for the budget – RUB 153 billion (Syroizhko et al., 2015).
The regional aspects of support for SME are studied by the example of Voronezh Oblast. At the level of a region, the system of support measures for entrepreneurship is implemented during realization of the Law “On development of small and medium entrepreneurship in Voronezh Oblast” (passed on March 12, 2008, No. 4-ОZ), state programs “Economic development and innovational economy” in the sub-program “Development and support for small and medium entrepreneurship”, “Development of entrepreneurship and trade for 2015-2021” in the part of the sub-program “Development and support for small and medium entrepreneurship”, “Development of industry and increase of its competitiveness” in the part of the sub-program “Creation and development of industrial clusters for 2016-2022”. Let us discuss the contents and realization of the state program “Economic development and innovational economy”, which supposes the following measures: information and consultation support for subjects of SME; development of the infrastructure of support for entrepreneurship; financial support for subjects of SME; support and development of youth entrepreneurship; creation of industrial parks; creation and provision of the activity of coordination center of support for export-oriented subjects of SME (Golikova et al., 2012).
The goals of the state program “Development of entrepreneurship and trade” are the following: creation of a favorable entrepreneurial climate and conditions for business, increase of effectiveness of state (regional) management in the spheres of development and support for SME and trade activity. Targeted indicators: turnover of products (services), manufactured by small companies, turnover of retail trade, and the total volume of economic activity of consumer cooperation organizations.
As a range of programs and sub-programs for support for SME have been implemented over a long period of time, let us view the intermediary results of their realization. This, the indicators of organizations’ demography have unstable dynamics. In 2005-2006, there was quick growth of the number of registered organizations – by more than 14 % in 2006, as compared to 2005. The period of 2006-2009 was marked by reduction of the number of registered organizations, and in 2009 this indicators reached its minimum for 2005-2015. Since 2010 there has been a gradual growth of the number of registered organizations, which is a positive tendency. The improving business climate in the region is shown by the reduction of the indicator of official liquidation of organizations (Figure 3).
Figure 3
Indicators of the demography of organizations of Voronezh Oblast for 2005-2015 [3]

According to the official statistics, provision of measures of state support for subjects of SME as of year-end 2014 allowed for the creation of 500 new jobs and preservation of 7,400 jobs. The turnover of organizations grew by 25% in 2015, as compared to 2013, with the companies of SME being concentrated in the sphere of retail and wholesale trade. At the same time, the turnover in the sphere of processing companies and agriculture grew, which is predetermined by support for SME in these sectors of economy (Serebryakova et al., 2016). Tax liabilities of the subjects of SME grew by 7 % in 2015, as compared to 2014 (Volkova & Volkova, 2016). The volumes of micro-financing grew by more than 25 % in the region (in 2014, the volume of micro-credits constituted RUB 174.4 million). This, a short analysis shows the effectiveness of realization of a complex of measures for supporting SME in the region.
An important tool of formation of the competitive policy in the region and activation of entrepreneurial activity is the Standard of competition development, which includes the stages of analysis and evaluation of competitive environment, development of measures for supporting the competition, and evaluation of the results of the performed events. It is supposed that the Standard will allow increasing the production of own-produced goods by 1.5 times, labor efficiency by 2 times by 2022, and the volume of investments into fixed capital – by 2.6 times.
There’s a Center for coordination of support for export-oriented subjects of small and medium entrepreneurship, which is important in the conditions of participation of the Russian Federation in the WTO and transborder position of Voronezh Oblast.
Despite the preservation of positive dynamics in the sphere of development of small and medium entrepreneurship, let us denote the problems that limit its development:
- high cost of clearing the administrative procedures;
- insufficient accessibility of financial resources necessary for entrepreneurship;
- insufficiency of measures of financial support for subjects of SME;
- insufficient knowledge of subjects of SME on the provided measures of state support.
Thus, it is obvious that subjects of SME need further support from the state and regions. This, the presidium of the Council with the President of the Russian Federation for strategic development and top-priority projects confirmed the Passport of the top-priority project “Small business and support for individual entrepreneurial initiative” (protocol dated November 21, 2016 No. 10). The project is to be realized from December 1, 2016 to March 1, 2019. The purpose of the project is provision of employment of the population by means of the number of unique subjects of SME (Tamoshina et al., 2012).
Besides, the decree of the Government of the RF dated June 2, 2016 No. 1083-r passed the “Strategy of development of small and medium entrepreneurship in the RF until 2030”. The document of strategic planning supposes full support for small and medium entrepreneurship (SME) from public authorities and sees the main goal as development of SME as a factor of innovational development and improvement of sectorial structure of economy, and, in the other hand – social development and provision of high level of employment (Federal portal of small and medium entrepreneurship; Sysoeva et al., 2015; Vertakova et al., 2016).
The necessity for creating the Strategy of development of SME is largely predetermined by low indicators of development of small and medium enterprises on the country. Thus, as to labor efficiency in this group, Russia is behind the industrially developed countries by 2-3 times. The share of SME has been reducing for such indicator as the share of turnover of enterprises in economy on the whole (reduction is more than 1.5 %). Also, the share of enterprises of small and medium business in the innovational sector is very low. Implementation of sanctions against the RF reflected the development of small business (Serebryakova et al., 2016).
The strategy determines the key parameters:
- increase of the turnover of SME by 2,5 times, as compared to 2014 (to RUB 104.7 trillion in 2030);
- growth of turnover per employee in the sphere of SME by 2 times (to RUB 4.6 million in 2030);
- increase of the share of processing industry in the turnover of SME (to RUB 20.9 trillion);
- growth of the number of the employed at the subjects of SME in the total number of the employed (to 35 %) (The federal portal of small and medium entrepreneurship).
For the purpose of realization of the tasks of the Strategy, the following measures will be taken:
- creation of a single center for support for SME, with the core being a joint-stock company “Federal corporation for development of small and medium entrepreneurship”, created by the Decree of the President of the Russian Federation dated June 5, 2015, No. 287 (The federal portal of small and medium entrepreneurship);
- creation of market niches for SME, which supposes development of competition in the markets (implementing the Standard of development of competition in the subjects of the RF and other measures, full support for socially-oriented SME (elimination of barriers for access to the social services market and other tools), expansion of demand for the products manufactured by SME (purchases from enterprises of small and medium business), development of trade and consumer market (E-trade, franchising, etc.);
- system of measures for provision of technological development, which includes the infrastructure for support for SME (e.g., creation of “innovational lift”), development of cooperation ties between subjects of SME and large companies of processing industry and high-tech services, support for export products of SME, and participation in realization of the National technological initiative, as well as stimulation of import substitution;
- creation of conditions for accessible financing (expansion of application of lease, factoring for SME, long-term financing, micro-financing, subsidizing, direct financing, etc.).
Apart from these methods, the following methods are viewed within the realization of the Strategy: predictability of fiscal policy with determination of a range of subsidies for subjects of SME, high quality of state regulation (in particular, reduction of controlling load), territorial development, realization of the regional policy for support for SME, training of employees for SME, determination of entrepreneurial potential (e.g., support for youth entrepreneurship) (Serebryakova et al., 2016).
In our opinion, further effective development of SME could be ensured by means of such tools as development of public-private partnership, which will raise the trust of business to the state; further development of small innovational entrepreneurship, including by means of expansion of venture business, provision of the system of subsidies to small innovational companies. An important condition is increase of the level of knowledge of SME on starting and developing business, further expansion of provision of the system of state guarantees. The state should stimulate the support and development of the competitive environment. A special attention should be paid to accumulation and development of human capital – for, whatever favorable are the created conditions for doing business, it is difficult to achieve success without human capital and the corresponding competences. The HR component is a decisive aspect in development of small and medium entrepreneurship – both at the state and regional levels.
Federal law “On development of small and medium entrepreneurship in the Russian Federation”, No. 209-FZ / Consultant Plus. [E-source]. Access: http://www.consultant.ru/cons/cgi/online.cgi?req=doc&base=LAW&n=193148&fld=134&dst=100255,0&rnd=0.09017238593521348#0
The federal portal of small and medium entrepreneurship [E-source]. Access: http://smb.gov.ru/measuresupport/legalregulation/
The official web-site of the Federal State Statistics Service. [E-source]. Access: http://www.gks.ru
Public wealth and mechanisms of its formation: monograph / G.I. Tamoshina, S.А. Volkova, Т.А. Volkova, М.О. Ryapolov. Voronezh: Nauchnaya Kniga Publ., 2012, 121 p.
Volkova S.А. Role of entrepreneurship in the system of provision of living standards of the population / S.А. Volkova, Т.А. Volkova // Modern economics: problems and solutions. - 2016. – No. 10.
Golikova G.V. Modernization of the Russian economy: problems and perspectives of strategic development / G.V. Golikova, N.V. Golikova, I.S. Naumov// Global problems of modernization of the national economy. Materials of the I International scientific and practical conference. Edited by V.M. Yuryev et al. - 2012. - P. 105-110.
Kaplan R.S. The Strategy Focused Organization: How Balanced Scorecard Companies thrive in the New Business Environment / R. S. Kaplan, D. P. Norton. - Harvard Business School Press. Boston, 2001. - Р. 32-34
Serebryakova N.A. Directions of transformation of labor in the modern conditions/ N.A. Serebryakova, N.V. Dorokhova, E.S. Dashkova, M.I. Isaenko// Journal of Applied Economic Sciences. Volume XI, Issue 8(46), Winter 2016. –P. 1542-1551.
Serebryakova N.A. Methodological approaches to evaluation of economic security of enterprise /N.A. Serebryakova, S.A. Volkova, T.A. Volkova, S.V. Semenenko // Journal of Applied Economic Sciences. Volume XI, Issue 2(40), Spring 2016. –P. 325-330.
Serebryakova N.A. Methodological Ways of Formation of Corporate Entities in Food Industry/ N.A. Serebryakova, S.V. Semenenko, N.V. Grishchenko // Journal of Applied Economic Sciences. Volume XI, Issue 4(42), Summer 2016. – P. 616-623/
Serebryakova N.A. Competitive Potential of Trade Organization: Theoretical and Methodological Foundations of Formation and Realization / N.A. Serebryakova, S.V. Semenenko, N.V. Grishchenko, T. Y. Ulchenko// European Research Studies, Volume XIX, Issue 2, 2016. – P. 3-11.
Syroizhko V.V. Features reflect the acquisitions of the companies in the consolidated financial statements in accordance with IFRS / V.V. Syroizhko, G.V. Golikova, D.N. Khorokhordin // Austrian Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences.- 2015. - № 1-2. - P. 217-222.
Sysoeva E.F. Influence of economic sanctions on the financial resources of russian organizations / E.F. Sysoeva, E. Budilova, I.E. Risin // Proceedings of the 2015 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference, CCDC 2015 - 27. 2015. - P. 1145-1156.
Treshchevsky Y.I. Methodological problems of the social projects' efficiency assessment / Y.I. Treshchevsky, M.B. Tabachnikova // Scientific result. Series: Economic studies. - 2015. - V. 1. – No. 4 (6). - P. 47-54.
Vertakova Y. The methodical approach to the evaluation and development of clustering conditions of socio-economic space / Y. Vertakova, I. Risin, Y. Treshchevsky // Innovation Management and Education Excellence Vision 2020: From Regional Development Sustainability to Global Economic Growth, IBIMA 2016. - Proceedings of the 27th International Business Information Management Association Conference. - 2016. - P. 1109-1118.
1. Voronezh State University, Voronezh, Russia
2. Voronezh State University of Engineering Technologies, Voronezh, Russia. e-mail: nad.serebryakova@mail.ru
3. Voronezh State University, Voronezh, Russia
4. Voronezh State Technical University, Voronezh, Russia
5. G.V. Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, Russia